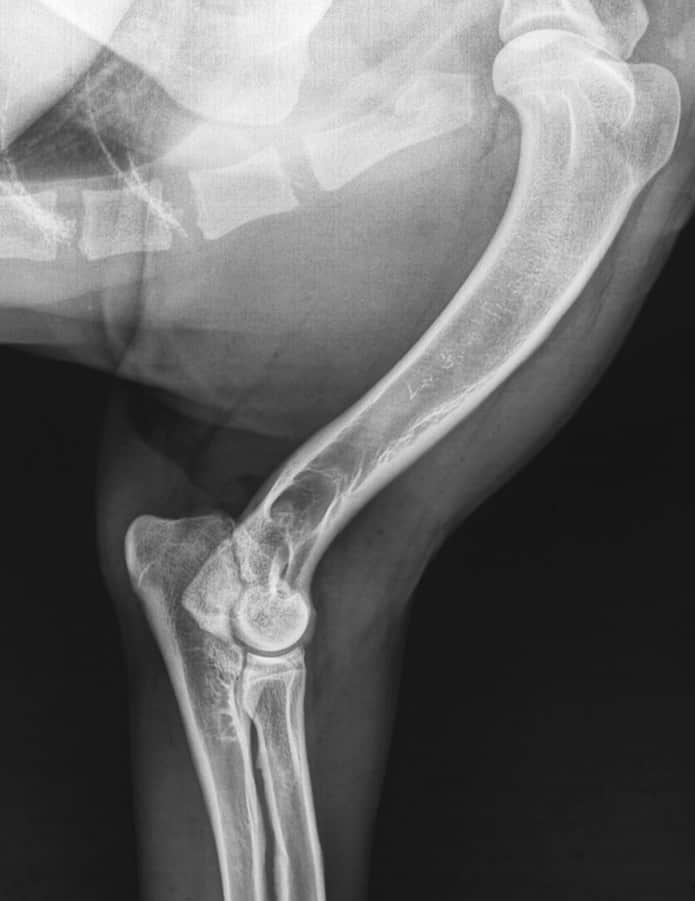
Elbow dysplasia is a common orthopedic condition affecting dogs, particularly large breeds. It can lead to chronic pain, decreased mobility, and a reduced quality of life for affected dogs. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for elbow dysplasia in dogs, as well as provide information on preventative measures and management strategies to help maintain your dog’s overall health.
What is Elbow Dysplasia?
Elbow dysplasia is a general term used to describe a group of developmental abnormalities that affect the elbow joint in dogs. These abnormalities can lead to joint instability, inflammation, and degenerative joint disease (arthritis) over time. The main components of elbow dysplasia include:
- Fragmented coronoid process (FCP)
- Osteochondritis dissecans (OCD)
- Ununited anconeal process (UAP)
- Elbow incongruity
These conditions can occur individually or in combination, leading to varying degrees of severity and clinical symptoms.
Causes of Elbow Dysplasia
The exact cause of elbow dysplasia in dogs is still not fully understood. However, several factors have been identified as potential contributors to the development of the condition:
- Genetics: Elbow dysplasia is considered to be a heritable condition, with certain breeds being more predisposed than others. Breeds commonly affected include Labrador Retrievers, Golden Retrievers, German Shepherds, Rottweilers, and Bernese Mountain Dogs.
- Nutrition: Overnutrition, particularly during the rapid growth phase of large-breed puppies, may contribute to the development of elbow dysplasia. Excessive intake of calories and certain nutrients, such as calcium, can lead to abnormal bone growth and joint development.
- Activity level: High-impact activities and excessive exercise during a dog’s growth phase may also play a role in the development of elbow dysplasia by placing increased stress on the developing joints.
Symptoms of Elbow Dysplasia
Symptoms of elbow dysplasia in dogs can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the specific components involved. Some common signs of elbow dysplasia include:
- Limping or lameness, often affecting one or both front limbs
- Stiffness, particularly after periods of rest or inactivity
- Pain or discomfort when extending or flexing the elbow joint
- Swelling around the elbow joint
- Decreased range of motion in the affected joint
- Reluctance to engage in activities that involve jumping or running
It is important to note that not all dogs with elbow dysplasia will exhibit overt clinical signs. In some cases, the condition may be detected during routine veterinary examinations or through diagnostic imaging for other reasons.
Diagnosing Elbow Dysplasia
Diagnosing elbow dysplasia in dogs typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic imaging. Your veterinarian will likely perform a thorough orthopedic examination, assessing your dog’s gait, range of motion, and checking for signs ofpain or discomfort in the affected joint(s). They may also ask about your dog’s medical history, including any previous injuries, exercise habits, and diet.
Diagnostic imaging, such as X-rays, is essential for confirming a diagnosis of elbow dysplasia and determining the specific components involved. Advanced imaging techniques, such as computed tomography (CT) scans or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), may also be used in some cases to obtain a more detailed view of the joint structures.
In addition to imaging, other diagnostic tests may be performed to rule out other potential causes of your dog’s symptoms, such as infections, trauma, or autoimmune disorders.
Treatment Options for Elbow Dysplasia
Treatment for elbow dysplasia in dogs depends on the severity of the condition, the specific components involved, and your dog’s overall health. Some common treatment options include:
- Conservative management: In mild cases or for dogs with minimal clinical signs, conservative management may be recommended. This approach typically involves weight management, controlled exercise, physical therapy, and the use of anti-inflammatory medications and joint supplements to help manage pain and inflammation.
- Surgical intervention: For more severe cases or dogs with significant clinical symptoms, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical options for elbow dysplasia vary depending on the specific abnormalities present and can include arthroscopic debridement, fragment removal, corrective osteotomies, and joint replacement. The goal of surgery is to improve joint function, alleviate pain, and slow down the progression of arthritis.
It is important to note that while treatment can help manage symptoms and improve your dog’s quality of life, there is no cure for elbow dysplasia, and affected dogs may continue to experience some degree of joint discomfort and mobility limitations throughout their lives.
Prevention and Management Strategies
While it may not be possible to completely prevent elbow dysplasia in dogs, there are several strategies that can help reduce the risk and manage symptoms in affected dogs:
- Responsible breeding practices: Choosing a reputable breeder who screens their breeding dogs for elbow dysplasia and follows breed-specific health guidelines can help reduce the risk of passing on this heritable condition.
- Proper nutrition: Feeding a balanced diet specifically designed for large-breed puppies can help prevent overnutrition and support healthy joint development during the critical growth phase.
- Controlled exercise: Encouraging low-impact activities and avoiding excessive exercise or high-impact activities during the growth phase can help reduce the risk of joint injuries and developmental abnormalities.
- Regular veterinary care: Routine veterinary check-ups can help detect and address any emerging orthopedic issues early, potentially reducing the severity and long-term impact of elbow dysplasia.
Conclusion
Elbow dysplasia is a complex and challenging orthopedic condition that can significantly impact a dog’s quality of life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, you can help manage your dog’s condition and provide the best possible care. Working closely with your veterinarian and following preventative measures can help maintain your dog’s overall health and wellbeing.
Relevant Sources:
- Orthopedic Foundation for Animals
- Davies Veterinary Specialists
- American College of Veterinary Surgeons
- National Institutes of Health
Arming yourself with knowledge about elbow dysplasia and partnering with your veterinarian can help ensure your dog receives the best possible care for this condition. By taking preventative measures and providing appropriate management strategies, you can help your dog maintain a higher quality of life and minimize the long-term impacts of elbow dysplasia.